Hard to port: India defies Washington’s pressure to deal with Iran

The sudden demise of Iranian President Ebrahim Raisi in a helicopter crash has not only created a power vacuum within Iran but also raised questions about the future of its foreign policy, especially in relation to the strategic Chabahar Port deal with India. This unexpected event comes at a critical juncture for Iran, which is embroiled in regional conflicts and struggling with severe economic challenges.
The transition of power, with the first vice-president Mohammad Mokhber stepping in temporarily, will significantly influence Iran’s international engagement, particularly in relation to its pivotal partnership with India.
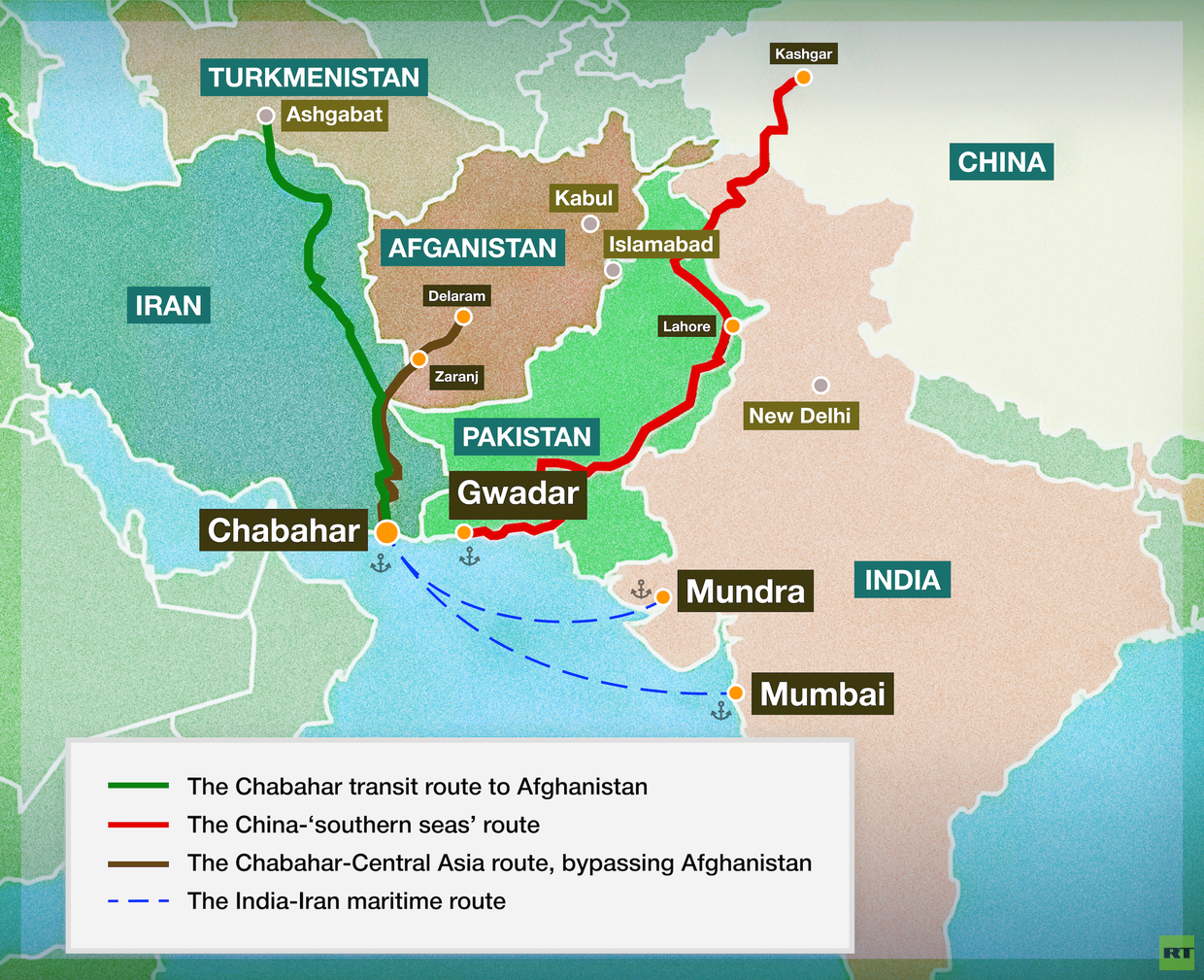
Chabahar Port, located in the Gulf of Oman, is a crucial element of India-Iran relations. It offers Delhi a strategic foothold in the region, providing a direct route to Afghanistan and Central Asia while bypassing Pakistan. The port not only serves as a gateway for India’s humanitarian assistance to Afghanistan, but also facilitates significant trade and commerce.
Furthermore, Chabahar Port is strategically positioned to integrate with the International North South Transport Corridor (INSTC), which spans from Russia to India. The INSTC is a collaborative effort involving India, Russia, Iran, and ten other Central Asian nations. This multimodal corridor seamlessly combines rail and sea transport, offering an alternative to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC). India’s economic interests in Chabahar Port revolve around enhancing trade, connectivity, and strategic positioning in the region.
So far, Chabahar Port has facilitated the trans-shipment of 2.5 million tons of wheat and 2,000 tons of pulses from India to Afghanistan. Additionally, in 2021, India provided Iran with 40,000 liters of an eco-friendly pesticide, Malathion, via the port to combat a locust infestation. The recent ten-year contract between India Ports Global Ltd (IGPL) and the Ports & Maritime Organisation of Iran (PMO) underscores the project’s importance to both nations.
Under the contract, IPGL is set to invest around $120 million for port operations and equipment. The collaboration in Chabahar is expected to continue beyond this period. India has also proposed a rupee credit line equivalent to $250 million for joint projects aimed at enhancing the port’s infrastructure.
The political instability following Raisi’s death introduces uncertainty, but there are strong indications that the Chabahar Port deal will continue to be a priority for Iran.
Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, who retains ultimate control over Iran’s state and foreign policy, remains in power, suggesting that foundational aspects of its foreign policy will persist despite the turmoil. The upcoming presidential election, expected to occur within 50 days, will be a decisive factor in shaping the continuity or change in Iran’s approach to its bilateral agreements.
India’s substantial investment in Chabahar Port, however, could be at risk. The United States has consistently warned of potential sanctions against countries engaging in business with Iran, which could complicate India’s efforts to secure necessary technologies and investment. These sanctions could also deter international companies from participating in the Chabahar project and hinder its development, as mentioned by US State Department spokesman, Vedant Patel.
Responding to the warning, Indian Minister of External Affairs Subrahmanyam Jaishankar exposed Washington’s “narrow view” of the deal. ”[The US] have not done so in the past. So, if you look at the US’ own attitude towards the port in Chabahar, the US has been appreciative of the fact that Chabahar has a larger relevance,” he noted.
However, it's notable that on November 8, 2018, India successfully secured a waiver from the US for the Chabahar project, with the justification being the need for access to Afghanistan.
Additionally, the fluctuating value of Iran’s rupee reserves, which has already impacted trade in commodities like rice, tea, and pharmaceuticals, might worsen due to political instability. A weakened Iranian economy would likely reduce its purchasing power, directly affecting Indian exports and bilateral trade volume. Therefore, Iran may not be able to afford as many imported goods from India, leading to a decrease in trade.
In May 2018, during the Trump administration, the US withdrew from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA). As a result, Indian imports of Iranian crude oil virtually ceased from nearly 12% of India’s total crude oil requirements. However, Chabahar Port and the railway line connecting it with Afghanistan remained exempt from US sanctions, allowing India to maintain its strategic investment and regional connectivity.
Chabahar Port is central to India’s strategy to counterbalance China’s influence in the region, particularly through the development of Pakistan’s Gwadar Port. This is located just 72km east of Chabahar, and is a key component of the BRI. It serves as a terminal for the CPEC, and is a 3,000km Beijing-backed infrastructure project in Pakistan, connecting China’s Xinjiang province to the Persian Gulf.
Any disruption to the development of Chabahar could weaken India’s strategic position and provide China with a stronger foothold in the region. India’s commitment to the port, as evidenced by the recent long-term agreement, highlights its strategic patience and vision for regional connectivity. However, the perceived risks associated with Iran’s political instability might also deter Indian businesses from further investment, potentially stalling key projects, in addition to US sanctions. These risks could be associated with Iran’s political instability, regional conflicts, and economic uncertainties.
The US response to Iran’s new leadership will play a significant role in determining the future of the Chabahar Port agreement. Historically, Washington has maintained a stringent stance on Iran due to concerns over nuclear proliferation and regional security. However, the death of Raisi might present an opportunity for the US to reassess its approach, particularly if the new Iranian leadership shows a willingness to engage in dialogue.
If Washington enforces sanctions rigorously, it could severely impact India’s involvement in Chabahar Port, hindering its broader regional strategy. However, recognizing the port’s role in supporting Afghanistan’s economy, the greater regional trade benefits, and countering Chinese influence, the US might adopt a more nuanced approach, balancing its policy objectives with strategic considerations.
The sudden change in Iran’s presidency could significantly impact stability of the Middle East, with potential repercussions for the operational security and economic viability of Chabahar Port. Its proximity to the volatile Strait of Hormuz, through which a substantial portion of the world’s oil transits, adds to its vulnerability in times of regional instability.
India must navigate this new geopolitical landscape with caution, ensuring that its strategic interests are protected. This involves closely monitoring Iran’s internal political dynamics, engaging diplomatically to reinforce the bilateral partnership, and adapting to evolving circumstances to maintain the momentum of the Chabahar project.
Despite Iran’s political turmoil, the bedrock of its foreign policy, especially its ties with India over Chabahar Port, is expected to remain unshaken. The strategic motives behind the Chabahar deal go beyond individual leadership, and are rooted in the wider geopolitical and economic interests of both countries. Regardless of Iran’s upcoming election results, Chabahar Port’s lasting strategic importance suggests that the bilateral agreement with India will persist as a crucial part of Tehran’s foreign policy.
India is likely to strategically re-engage with the US to maintain the Chabahar Port’s waiver, emphasizing the broader regional advantages and extensive implications for the region’s prosperity. As noted by S. Jaishankar, this forward-thinking strategy would not only serve India’s interests but also promote a broader vision of regional growth and cooperation, surpassing narrow interests.
The statements, views and opinions expressed in this column are solely those of the author and do not necessarily represent those of RT.

















