Censorship war: Website unmasks links Google is blocking from search results
Published 17 Jul, 2014 00:40 | Updated 18 Jul, 2014 16:53
A subversive website has been launched to keep track of news and other webpages Google has “censored” from the search engine’s index, following the European Court of Justice’s controversial Right to be Forgotten ruling.
The tech giant has reportedly been inundated with 70,000 requests to remove sensitive information from its search results in the aftermath of the ECJ’s decision. While this data may be accurate, it is considered “irrelevant” and possibly defamatory under the EU policy shift.
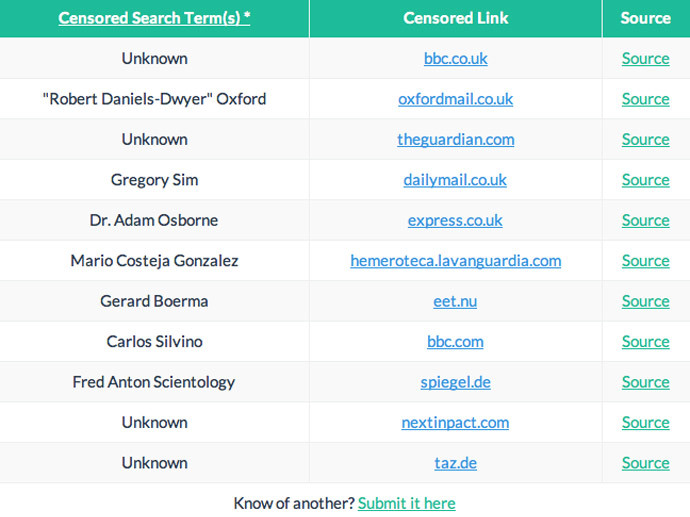
In a mark of protest against online censorship, a new site ‘Hidden From Google’ has begun archiving links censored by search engines intent on complying with ECJ demands. The site was set up by US web developer and transparency advocate, Afaq Tariq.
The New Jersey developer asserts the removal of links from a search engine’s index amounts to censorship. So in an effort to preserve transparency in Europe’s online realm, he invites visitors to log data that has been removed from Google on the site.
“This list is a way of archiving the actions of censorship on the Internet,” Tariq states on the site’s about page. “It is up to the reader to decide whether our liberties are being upheld or violated by the recent rulings by the EU.”
Following the ECJ’s ruling in May, Google allows European users to request the deletion of data referencing them if they consider it irrelevant or outdated. Implementing the ‘right to be forgotten’ ruling has proven difficult for Google, however, despite the firm's creation of a special advisory committee to assist in the process.
Ironically searches conducted in Europe for information the tech firm has censored are returning links to Tariq's site.
Google says that when evaluating users’ requests, it checks “whether the results include outdated information” and if the data relates to the public interest. Thus far, requests tendered to the tech company for consideration under the EU ruling relate to financial fraud, violent crime, child pornography arrests and more.
Google retains the power to reject data removal applications in cases where the public interest is deemed to trump individuals’ right to privacy. But such a position of power is arguably more appropriate for a state body than a mammoth commercial firm.
“Here state power is being exercised without the involvement of the state: Google decides how to handle redaction requests”, Johnathan Zittrain, a professor of law and computer science at Harvard University, recently told the Financial Times.
“If a search engine declines to alter its results, the claimant might appeal to a national data protection authority. Under the court’s decision, the public’s right to know is to be balanced against a claimant’s right to privacy – but there is no easy way for the public to remonstrate against poor balancing”, he said.
While Tariq’s site creates a degree of transparency, independent and comprehensive scrutiny of how this new EU right operates in practice is warranted. Zittrain proposes Google and its peers should contribute to “an independent database of takedowns”. But such a move is far from EU-wide implementation.














