Bigger than Apophis: Dangerous 300+ meter asteroid to cross Earth orbit every 3 years

Scientists have calculated that 2014 UR116 asteroid will fly in dangerous proximity to Earth every three years. If it collides with the planet the energy of the explosion could be a thousand times greater than the impact of the Chelyabinsk meteorite.
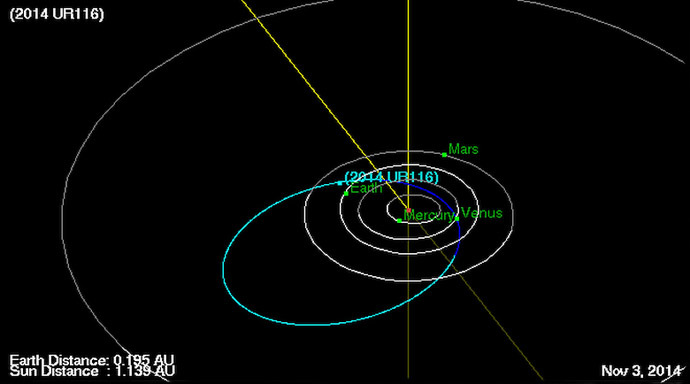
Vladimir Lipunov, a leading scientist on the team which discovered the asteroid this October, says the scientists now know its orbit and its period which is 3 years, but they cannot say precisely when the asteroid will approach the Earth.
“We should track it constantly. Because if we have a single mistake, there will be a catastrophe. The consequences can be very serious,” he said in the documentary “Asteroids attack” posted on Roscosmos website.
The new asteroid, called 2014 UR116 is about 370 meters in diameter. Its size exceeds the famous Apophis which the Earth can meet in the next decade. The exact trajectory of 2014 UR116 is yet to be determined, but theoretically it may collide with the Earth, Mars or Venus. Its trajectory can fluctuate because of the gravitational pull of these planets.
READ MORE: 1,000 times stronger than Chelyabinsk meteorite: New asteroid may threaten Earth
Some specialists believe we can be sure for a certain period of time that no collision will happen. Viktoria Damm from the Siberian Geodesic Academy Planetarium told TASS news agency that when the asteroid flies near Mars, its trajectory may change. That’s why the time of approach is unknown but she believes it will not happen in the coming two years.
In case of a collision with the Earth the energy of the explosion could be a thousand times greater than the Chelyabinsk meteorite. When a meteorite burst above the city of Chelyabinsk in February 2013, the impact was estimated to be equivalent to 440-500 kilotons of TNT. But the Chelyabinsk meteorite was relatively small, about 17 meters in diameter and it disintegrated with a blast at an altitude of over 20 kilometers.
It is also important to define the composition of an asteroid. If it consists of stone it generally breaks into small parts, but metal asteroid can reach the surface of Earth, according to Stanislav Korotky, Ka Dar observatory scientific director. The famous Arizona crater is the track of a metal asteroid.
The Chelyabinsk meteorite prompted the scientists to fully engage in projects of space security. Russian space agency Roscosmos plans to work out a special system to stand against dangerous asteroids by 2025. The agency wants to use new technologies to change the orbits of asteroids, including different kinds of robots, for instance, robots-cleaners to take away the space rubbish from Earth orbit.
Meanwhile, NASA is working on projects Orbita@home and Spacewatch and plans to deploy The Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Last Alert System (ATLAS) in 2015.
The asteroid 2014 UR116 was discovered with the help of Russia's network of robotic telescopes which perform the sky survey without human direction and can create its own data bases.














