First head transplant possible within two years, says Italian ‘Frankensurgeon’
Controversial Italian neurosurgeon Sergio Canavero claims he could perform the world’s first ever human head transplant in 2017, despite ethical and scientific reservations from many of his colleagues.
“The Wright brothers flew their first plane when every so-called expert in the world thought that this was impossible. So, I don’t believe the word ‘impossible’ – I have been working on this project for 30 years, and the technology is now there,” Canavero, who heads the Turin Advanced Neuromodulation Group, told Sky News.
Canavero’s team, which previously touted their plans for a whole-eye transplant, published a paper outlining the procedure two years ago, and say they are now ready to find subjects for the experimental procedure.
"If society doesn't want it, I won't do it. But if people don't want it in the US or Europe, that doesn't mean it won't be done somewhere else,” the neurosurgeon told the New Scientist.
Prior to the surgery, the two bodies would be cooled, to preserve them better without oxygen, and then their necks would be sliced open and major blood vessels connected between the donor’s body and the recipient’s head.
The key stage would be the severing and re-attachment of the spinal cord, which would have to be cleanly sliced, and would then present two “spaghetti-like” bundles of nerves, which would need to be connected to each other. Canavero foresees this being done with polyethylene glycol, a material that enables fat in different tissues to mesh.
The neck would then be stitched shut, and the patient placed in an artificial coma for four weeks, allowing the body to heal without movement.
Canavero previously estimated that the pioneering surgery would cost upwards of €10 million, and that the perfect initial recipient would be a person with a young, healthy brain, suffering from muscular dystrophies or metabolic disorders. He proposes initial experiments where both of the individuals in the surgery would be brain-dead.
‘No evidence’ it would work
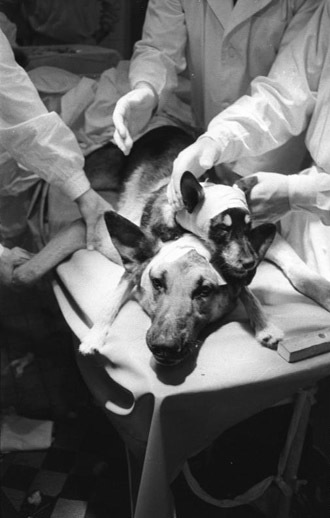
Most of the scientific objections to the procedure focus on the impossibility of restoring body control after the refusing of the spine. Currently, it is commonly impossible to overcome paralysis when a spinal cord is completely severed, even when the rest of the body belongs to the same person. An ambitious procedure performed by Polish doctors last year, managed to restore movement by implanting lab-grown nerve cells into the spine.
But Richard Borgens, director of the Center for Paralysis Research at Purdue University, Indiana, said that Canavero’s surgery offers no such guarantees.
"There is no evidence that the connectivity of cord and brain would lead to useful sentient or motor function following head transplantation,” he told the New Scientist.
"This is such an overwhelming project, the possibility of it happening is very unlikely. I don't believe it will ever work, there are too many problems with the procedure. Trying to keep someone healthy in a coma for four weeks – it's not going to happen," said Harry Goldsmith, a clinical professor of neurological surgery at the University of California, Davis, himself a leading expert on reconnecting spinal tissue that enables paralyzed people to walk again.
Yet Canavero can reassure himself that his ‘Frankensurgery’ is not without precedent. The first attempted dog head transplant dates back to more than a century ago, and Soviet scientist Vladimir Demikhov performed multiple such procedures in the 1950s. US surgeon Robert J. White famously performed a head transplant between two monkeys in 1970, with the survivor living for nine days.
READ MORE: Paralyzed man walks again thanks to UK-funded tech
In all of the previous procedures, the recipients remained paralyzed, and all struggled with immune rejection of the new body parts, though with improved techniques, this is not an insurmountable problem.
Ethical problems – from religious considerations, to the simple ickiness-factor – are also likely to slow down progress.
"I believe that what is specifically human is held within the higher cortex. If you modify that, then you are not the same human and you should question whether it is ethical. In this case, you're not altering the cortex," said Patricia Scripko, a neurologist and bioethicist at the Salinas Valley Memorial Healthcare System in California, who does not believe the procedure is possible, but insists it is not objectionable.
READ MORE: Mind-controlled bionic hand using nerve transplants restores function
"If a head transplant were ever to take place, it would be very rare. It's not going to happen because someone says 'I'm getting older, I'm arthritic, maybe I should get a body that works better and looks better'."
Despite the myriad objections – and even his supporters are skeptical of the two-year timeframe – Canavero will now have the chance to convince his colleagues, when he will present his specific plans for the surgery to the prestigious congress of the American Academy of Neurological and Orthopedic Surgeons in Maryland in June.
"I first spoke about the idea two years ago, to get people talking about it. I'm trying to go about this the right way, but before going to the moon, you want to make sure people will follow you," he said.














